4G Wireless Handover
Consider the scenario, where a mobile phone connected to a base station (source) is streaming a video from the internet, and the mobile phone is going to switch to a closer base station (target) without interrupting their video stream. This process (called a handover) is shown in the diagram below.
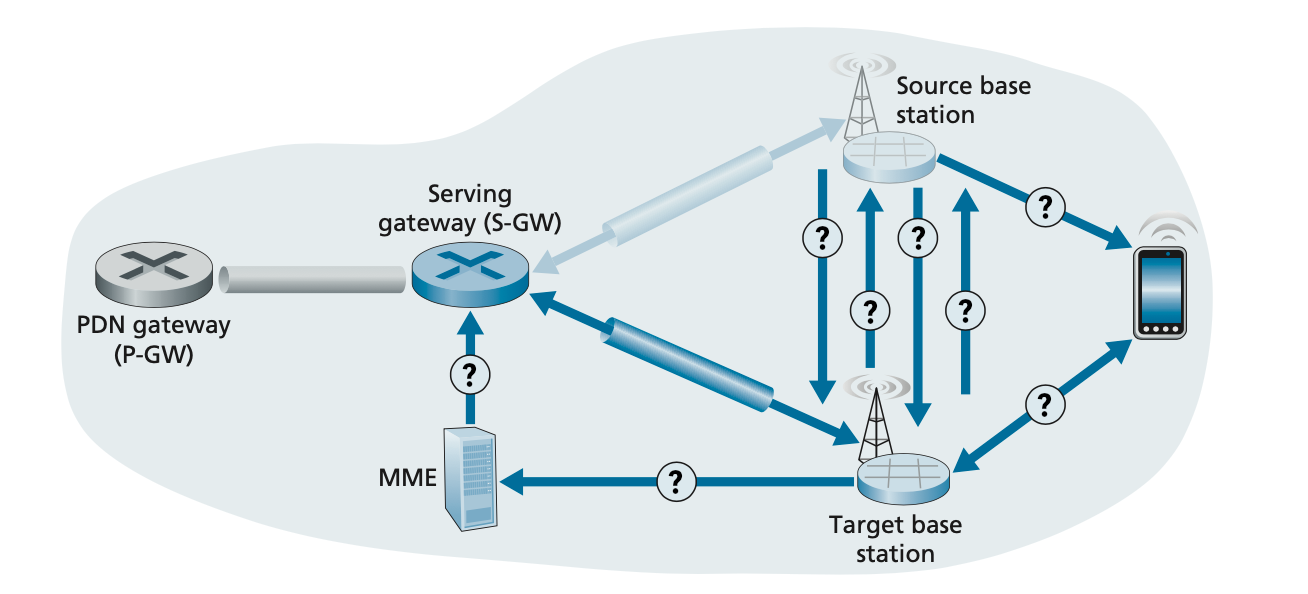
Take a look at the statements below and put them in the correct order.
- The source base station receives the Handover Request Acknowledgement message and informs the mobile device of the target base station’s identity and channel access information. At this point, the mobile device can begin send- ing/receiving datagrams to/from the new target base station. From the mobile device’s point of view, handover is now complete! However, there is still a bit of work to be done within the network.
- The target base station checks whether it has the resources to support the mobile device and its quality of service requirements. If so, it pre-allocates channel resources (e.g., time slots) on its radio access network and other resources for that device. This pre-allocation of resources frees the mobile device from having to go through the time-consuming base-station association protocol discussed earlier, allowing handover to be executed as fast as possible. The target base station replies to the source base station with a Handover Request Acknowledge message, containing all the information at the target base station that the mobile device will need to associate with the new base station.
- The source base station will also stop forwarding datagrams to the mobile device and instead forward any tunneled datagrams it receives to the target base station, which will later forward these datagrams to the mobile device.
- The target base station informs the MME that it (the target base station) will be the new base station servicing the mobile device. The MME, in turn, signals to the Serving Gateway and the target base station to reconfigure the Serving- Gateway-to-base-station tunnel to terminate at the target base station, rather than at the source base station.
- At this point, the target base station can also begin delivering datagrams to the mobile device, including datagrams forwarded to the target base station by the source base station during handover, as well as datagrams newly arriving on the reconfigured tunnel from the Serving Gateway. It can also forward outgo- ing datagrams received from the mobile device into the tunnel to the Serving Gateway.
- The current (source) base station selects the target base station, and sends a Handover Request message to the target base station.
- The target base station confirms back to the source base station that the tunnel has been reconfigured, allowing the source base station to release resources associated with that mobile device.
Question List
1. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the first step in the handover process?
2. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the second step in the handover process?
3. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the third step in the handover process?
4. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the fourth step in the handover process?
5. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the fifth step in the handover process?
6. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the sixth step in the handover process?
7. Which lettered step (A-G) above corresponds to the seventh and final step in the handover process?
Solution
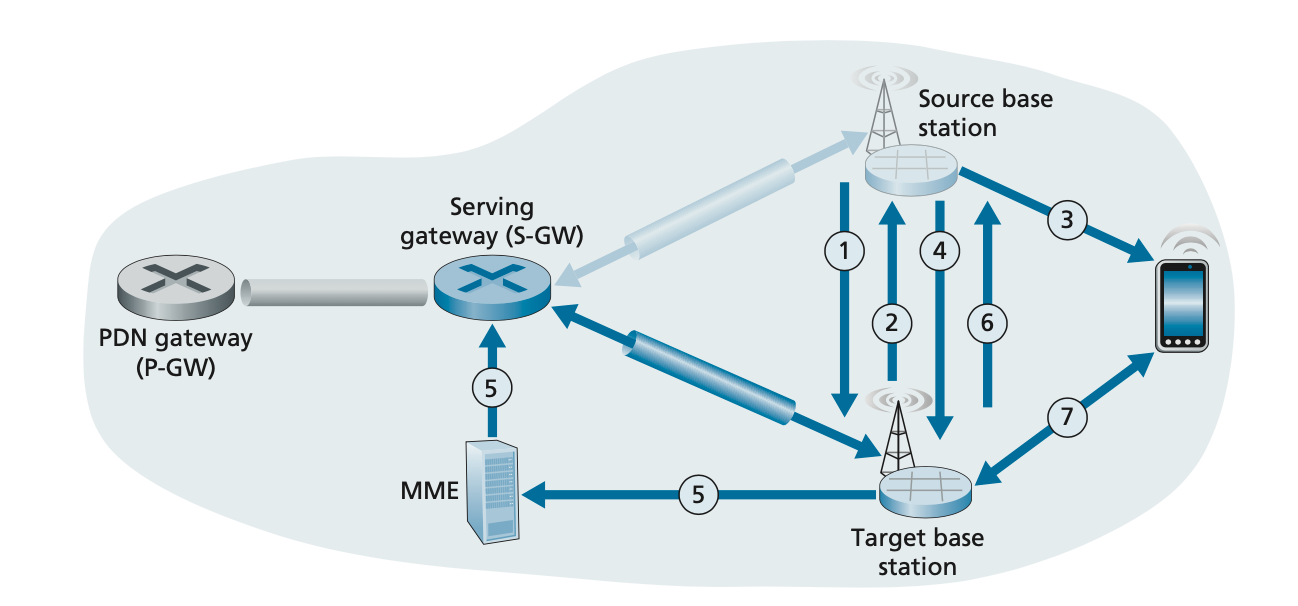
1. The first step corresponds to F
2. The second step corresponds to B
3. The third step corresponds to A
4. The fourth step corresponds to C
5. The fifth step corresponds to D
6. The sixth step corresponds to G
7. The seventh and final step corresponds to E
That's incorrect
That's correct
The answer was: F
The answer was: B
The answer was: A
The answer was: C
The answer was: D
The answer was: G
The answer was: E